
Trypan Blue is an azo dye used to selectively stain dead cells and tissues blue. It is synthesized from toluidine and was first introduced in 1904 by German scientist Paul Ehrlich during his research on African trypanosomes.
This dye is commonly used in cell viability assays and cell counting protocols, as it selectively stains non-viable cells. A 0.4% Trypan Blue solution is one of the most widely used dyes in the dye exclusion method.
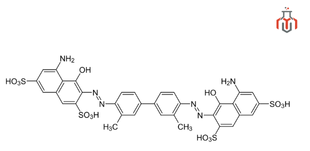
CAS No.:72-57-1
Synonyms: Diamine Blue, Niagara Blue, Naphthylamine Blue, Azidine Blue 3B
Resources: Biological Stains | Classification, Examples & Uses
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C₃₄H₂₄N₆Na₄O₁₄S₄ |
| Molecular Weight | 960.8 g/mol |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Solubility | Soluble in water |
| Storage | Store at 15–30°C |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | Bluish-gray to dark blue |
| State | Crystalline powder |
| Melting point | Decomposes above 300 °C |
| λmax | ~607 nm (in methanol) |
| pH | ~6.8 to 7.2 |
| Pictograms : |  |
| Hazard Statements : | H350: May cause cancer |
| Precautionary statements : | P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood |
Trypan Blue is an azo dye used to selectively stain dead cells and tissues blue. It is synthesized from toluidine and was first introduced in 1904 by German scientist Paul Ehrlich during his research on African trypanosomes.
This dye is commonly used in cell viability assays and cell counting protocols, as it selectively stains non-viable cells. A 0.4% Trypan Blue solution is one of the most widely used dyes in the dye exclusion method.

CAS No.:72-57-1
Synonyms: Diamine Blue, Niagara Blue, Naphthylamine Blue, Azidine Blue 3B
Resources: Biological Stains | Classification, Examples & Uses
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C₃₄H₂₄N₆Na₄O₁₄S₄ |
| Molecular Weight | 960.8 g/mol |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Solubility | Soluble in water |
| Storage | Store at 15–30°C |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | Bluish-gray to dark blue |
| State | Crystalline powder |
| Melting point | Decomposes above 300 °C |
| λmax | ~607 nm (in methanol) |
| pH | ~6.8 to 7.2 |
| Pictograms : |  |
| Hazard Statements : | H350: May cause cancer |
| Precautionary statements : | P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood |
Trypan blue is used to check cell viability, for exclusion assays, for checking the cytotoxic effects of various compounds, and in ophthalmic surgery.
Trypan blue is considered hazardous due to its carcinogenic and mutagenic effects. It may affect reproduction and swelling of compromised cells.
Trypan Blue and Methylene Blue are not the same compound; they both have different chemical classes and applications. Trypan Blue is an azo dye compound, primarily used for cell viability assays, while Methylene Blue is a thiazine dye, commonly used for staining cellular components like nuclei in microbiology and histology.
Trypan blue is inhibited by live cells but able to penetrate the compromised membranes of dead cells and stain them blue and making it distinguishable.
Trypan Blue solution (0.4 %) is used to identify dead cells in cytotoxicity and cell viability assays. It selectively stains non-viable cells, making it ideal for use with hemocytometers or automated cell counters in research and diagnostic labs.
Trypan Blue may be toxic and is a suspected mutagen and carcinogen, requiring careful handling. It can also cause non-specific staining, and its inability to distinguish early apoptotic cells limits its use in detailed viability studies.
Trypan Blue is unable to stain healthy and live cells. However, if red blood cells get damaged or lysed, they may absorb the dye and appear blue.
Trypan Blue is a membrane-impermeable dye; it cannot pass the intact membrane of a living cell, while dead cells have compromised or ruptured membranes, allowing the dye to enter and bind intracellular components, resulting in blue coloration.