
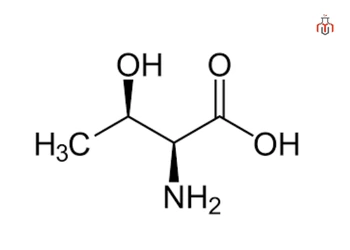
Threonine is an essential amino acid, meaning the body cannot produce these amino acids and must be consumed through diet. It is a building block of the proteins, supports elastin and collagen for bone and muscle strength. Threonine supports the immune system, metabolism as it is a precursor to other amino acids like serine and glycine. It is commonly found in plants, sesame seeds, meat, egg, cottage cheese, lentils and black turtle beans.
CAS No.: 72-19-5
Synonyms: L-(-)-Threonine, (2S,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid, L-(-)-Threonine, (2S,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid, Threonin, (S)-Threonine, 2-amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid, Treonina, (2S,3R)-2-Amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid, Threoninum, L-Threonin, L-thr, (2S)-threonine, (2S,3R)-(-)-Threonine, L-alpha-Amino-beta-hydroxybutyric acid, L-2-Amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C4H9NO3 |
| IUPAC name | (2S,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid |
| Molecular weight | 119.12 g/mol |
| Solubility | Insoluble in ethanol, ether ether, and chloroform |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | White |
| State | Crystals Powder |
| Melting point | 256 °C (Decomposes) |
| pH | 5-6.5 |
| Vapour density | 0.00000004 [mmHg] |
| LogP | -2.94 |
Threonine is generally safe under medical supervision, but there may be possible side effects that occur in some individuals.
Side Effects
| Pictograms : | Not Available |
| Hazard Statements : | Not Available |
| Precautionary statements : | Not Available |
Threonine is an essential amino acid, meaning the body cannot produce these amino acids and must be consumed through diet. It is a building block of the proteins, supports elastin and collagen for bone and muscle strength. Threonine supports the immune system, metabolism as it is a precursor to other amino acids like serine and glycine. It is commonly found in plants, sesame seeds, meat, egg, cottage cheese, lentils and black turtle beans.

CAS No.: 72-19-5
Synonyms: L-(-)-Threonine, (2S,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid, L-(-)-Threonine, (2S,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid, Threonin, (S)-Threonine, 2-amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid, Treonina, (2S,3R)-2-Amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid, Threoninum, L-Threonin, L-thr, (2S)-threonine, (2S,3R)-(-)-Threonine, L-alpha-Amino-beta-hydroxybutyric acid, L-2-Amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C4H9NO3 |
| IUPAC name | (2S,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid |
| Molecular weight | 119.12 g/mol |
| Solubility | Insoluble in ethanol, ether ether, and chloroform |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | White |
| State | Crystals Powder |
| Melting point | 256 °C (Decomposes) |
| pH | 5-6.5 |
| Vapour density | 0.00000004 [mmHg] |
| LogP | -2.94 |
Threonine is generally safe under medical supervision, but there may be possible side effects that occur in some individuals.
Side Effects
| Pictograms : | Not Available |
| Hazard Statements : | Not Available |
| Precautionary statements : | Not Available |
Threonine is polar amino acid as its side chain contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) that form hydrogen bonds, making it more soluble in water than non-polar amino acids.
Threonine is neither acidic nor basic; it is a neutral, polar amino acid. Its side chain contains a hydroxyl (–OH) group that makes threonine polar and hydrophilic.
Threonine’s side chain does not carry a charge at normal pH values, and is therefore considered non-ionizable in nature.