
- What are Preservatives in Cosmetics?
- Why are Preservatives necessary in Cosmetics?
- Types of Preservatives Used in Cosmetics
- List of Commonly Used Preservatives in Cosmetic Formulations
- Preservatives and Regulatory Compliance
- Safe Use of Preservatives in Cosmetic Formulations
- Restricted Preservatives in Cosmetic Formulations
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What are Preservatives in Cosmetics?
In cosmetic and beauty product formulations, a variety of other materials are added apart from the main active ingredients, such as emollients, humectants, chelating agents, colorants, fragrances, and preservatives to improve its appearance, effectiveness, and shelf life.
Preservatives in cosmetics are substances added to cosmetic formulation to maintain pH, prevent microbial contamination, improve product life, and maintain formulation stability. In regulatory terms, a preservative is a substance of natural or synthetic origin intended to inhibit the development of microorganisms.
Preservatives are commonly used in cosmeceutical products such as fragrances, lipsticks, shampoos, creams, hair care products, and body washes.
Why are Preservatives necessary in Cosmetics?
Preservatives are essential in cosmetics because many products contain water and organic, nutrient-rich ingredients, which favour microbial growth. Cosmetic products also have a neutral pH range, and they provide an environment particularly susceptible to the survival and growth of microorganisms. Exposure to air, moisture, heat, and repeated consumer use further increases the risk of contamination. Products of cleaning and bathing are commonly stored in domestic bathrooms, where there is a high chance of contamination due to moisture, humidity, and darkness. Without preservatives, cosmetic products can spoil quickly, leading to changes in texture, color, odor, and effectiveness.
By restricting microbial fermentation, preservatives protect consumers from potential skin infections, irritation, and adverse reactions, ensuring that cosmetic and personal care products remain safe and effective from the time of manufacture until the last use.
Types of Preservatives Used in Cosmetics
Based on the origin and method of synthesis, cosmetics preservatives are categorised mainly into two natural (naturally derived) and artificial (synthetic).

Natural preservatives
Natural preservatives are compounds which are directly obtained from nature and are pure and organic. It is mainly plant juice and natural oils, and valued for their inherent antimicrobial property and compatibility with skin.
Sources of Natural Preservatives
Natural preservatives are primarily derived from vegetables, fruits, and plant-based raw materials such as-
- Plant Extracts – Grapefruit seed extract, rosemary extract
- Essential oils – Tea tree oil, Neem oil, Thyme oil
- Vitamins – Vitamin E (Tocopherol) and Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Artificial (Synthetic) preservatives
Unlike natural preservatives, artificial preservatives are chemically engineered products designed to remain effective under a wide range of temperatures, pH, and moisture. It is a combination of two or more chemicals to enhance efficacy and give a synergistic effect on the formulation.
List of Commonly Used Preservatives in Cosmetic Formulations
Potassium Sorbate
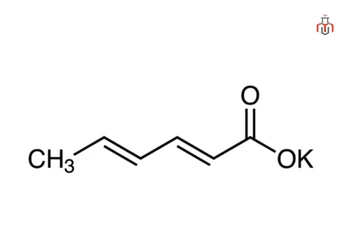
Potassium sorbate is the potassium salt of sorbic acid, produced by neutralizing sorbic acid with potassium hydroxide. It appears as a crystalline powder and is widely used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products. Potassium sorbate is particularly effective against yeast and molds and is suitable for water-based and low-pH formulations.
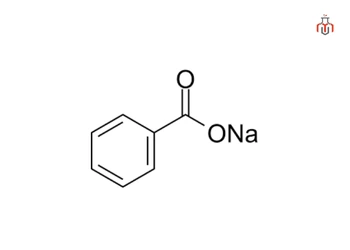
Sodium Benzoate
Sodium Benzoate (C₆H₅COONa) is an aromatic carboxylic acid salt. It is a water-soluble preservative suitable for aqueous and water-based formulations and helps to inhibit the growth of bacteria, yeast, and fungi, making it suitable for a broad range of formulations. It is also used in combination with other preservatives or preservative boosters to improve broad-spectrum antimicrobial protection.
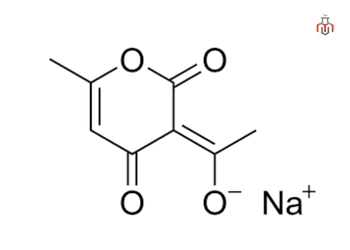
Sodium Dehydroacetate
Sodium Dehydroacetate (SDA) is a water-soluble sodium salt of dehydroacetic acid (DHA) widely used in cosmetic and personal care formulations for its high-efficacy antimicrobial and fungicidal properties. It provides effective protection against a broad range of microorganisms, including bacteria, yeasts, and molds, thereby helping to prevent product spoilage and extend shelf life.
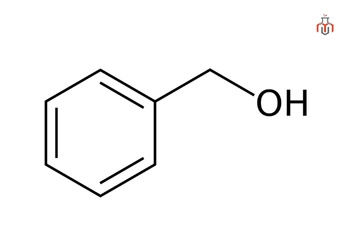
Benzyl Alcohol
Benzyl alcohol (C₆H₅CH₂OH) is an aromatic alcohol that appears as a colorless liquid with a mild, pleasant aroma. It is widely used in industrial, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic applications. Functioning as both a solvent and a preservative, benzyl alcohol helps improve the solubility of compounds and extends the shelf life of cosmetics and personal care products.
Benzyl alcohol is commonly synthesized from toluene or benzyl chloride, making it a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis and a valuable ingredient in various formulations.
Glyceryl Caprylate
Glyceryl caprylate is a naturally derived monoester of glycerin and caprylic acid (C8 fatty acid) used in cosmetics, personal care, and pharmaceutical formulations due to its multifunctional properties. It helps extend the shelf life of products by inhibiting microbial growth, while also enhancing the texture and feel of formulations by softening and smoothing the skin. Its gentle nature makes it suitable for sensitive skin.
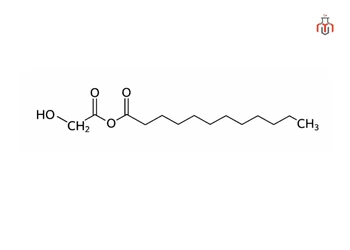
Glyceryl Undecylenate
Glyceryl Undecylenate is an ester formed from glycerol (glycerin) and undecylenic acid, a naturally occurring fatty acid. It can be extracted from castor oil (which provides the undecylenic acid) and glycerin derived from rapeseed or other plant oils.
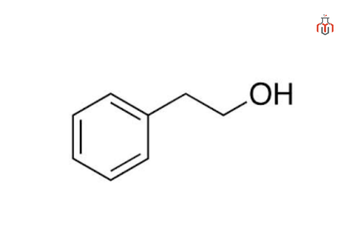
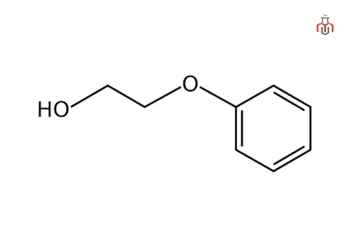
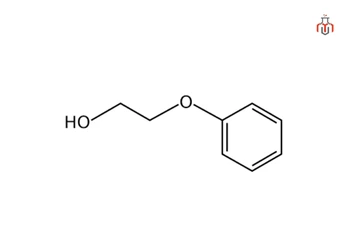
Phenethyl Alcohol
Phenethyl alcohol, also known as 2-phenylethanol (C₆H₅CH₂CH₂OH), is an aromatic alcohol used in the formulation of eye area makeup, makeup products, skin care products, shampoos, perfumes, and colognes. It helps to prevent or retard bacterial growth, and thus protects cosmetics and personal care products from spoilage.
1, 2-Hexanediol
1,2 -Hexanediol is a colorless synthetic preservative that forms a layer on the skin and helps to retain moisture. It promotes the easy absorption of cosmetic products, leaving the skin surface smooth and resilient.

Ethylhexylglycerin
Ethylhexylglycerin is a multifunctional, glycerin-derived compound widely used as a preservative booster, humectant, and emollient. It enhances antimicrobial properties and deodorising efficacy of the product. It is very easily soluble in cosmetics, alcohols, and glycols as well as oils.
For a more detailed understanding of its functional role in skin and hair care products, read: Ethylhexylglycerin in Skin & Hair Care | Uses and Side Effects
Phenoxyethanol
Phenoxyethanol, also known as 2-phenoxyethanol, is an aromatic glycol ether that has a large spectrum of microbial activity and is effective against various gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It is added to rinse-off and leave-on cosmetic products due to its stability and formulation versatility.
Preservatives and Regulatory Compliance
FDA Regulations for Cosmetic Preservatives (USA)
In the United States, the Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR), led by a panel of medical experts, collaborates with the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to provide a review and assessment of the safety of ingredients used in cosmetics. But the FDA does not maintain an approved list of cosmetics preservatives like the EU. Manufacturers are legally responsible for product safety, and preservatives must be safe for their intended use under labelled or customary conditions.
In the U.S., cosmetics and preservatives are regulated under
- Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act)
- Fair Packaging and Labelling Act (FPLA)
- 21 CFR parts 700-740 (Cosmetics regulation)
It is the responsibility of the FDA to prohibit the distribution of adulterated or mislabeled cosmetics if they are found to be unsafe and mislabeled.
EU Cosmetic Regulation and Restricted Substances
Unlike the U.S., in the European Union, all cosmetics preservatives are regulated under Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009, and only preservatives listed in Annex V are permitted with mandatory warning statements, Usage restrictions, and INCI name declaration.
Safe Use of Preservatives in Cosmetic Formulations

Characteristics of an Effective Preservative
- Preservatives should be of broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and effective against bacteria, yeast, and mold.
- It must remain effective throughout the anticipated shelf life.
- Preservatives should be liquid and water-soluble, as there are high chances of microbial growth in the aqueous phase.
- It should be effective over a wide range of pH.
- It must be compatible with other formulation ingredients and should not get deactivated or compromised by other raw materials in the formulation.
- An ideal preservative should be odorless and colorless, ensuring no impact on the product’s physical appearance.
- It must be toxicologically safe and approved for cosmetic use.
Key Considerations for Preservative Selection and Use
- The concentration of preservatives does not exceed the regulatory limits.
- Chemical interaction(Impact of pH, temperature) must be checked before adding preservatives in formulation.
- The quality of the preservative material must also be checked.
- Compatibility testing is essential, as certain preservatives cannot be used with specific ingredients.
- Check the spectrum of action, such as some highly effective on bacteria and some on yeast or mold.
- Preservatives should be sourced exclusively from trusted suppliers with cGMP-compliant manufacturing practices.
Restricted Preservatives in Cosmetic Formulations
Some preservatives have negative effects on the skin, may cause irritation, red patches, hives, and even it may lead to skin cancer. These preservatives are often of low quality and low-cost alternatives to advanced preservatives. Certain preservatives are allowed only within safety limits, such as formaldehyde and triclosan.
Commonly Restricted Preservatives
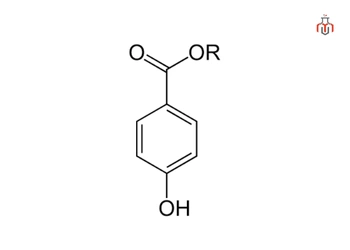
Parabens
Parabens are alkyl esters of p-hydroxybenzoic acid, widely used in cosmetic formulations. Their antimicrobial activity is primarily attributed to their ability to disrupt microbial cell membranes and inhibit key enzymatic processes essential for nucleic acid synthesis. While some parabens remain permitted, log-chain parabens are restricted due to endocrine disruption concerns.
Isothiazolones
Methylchloroisothiazolinone and methylisothiazolinone are highly effective preservatives but are restricted primarily to rinse-off products (0.0015%) due to their potential to cause skin sensitization.
Phenolic compounds
The most common Phenolic preservatives used in cosmetics and personal care are phenoxyethanol and benzyl alcohol. Phenoxyethanol functions as a preservative and a solvent, and it is often combined with other preservatives to provide broad spectrum microbial effect. Benzyl alcohol is a colorless liquid with a mild, pleasant odor and has similar mechanisms of action like phenoxyethanol. It is generally permitted for use at a maximum concentration of up to 1%, according to regulatory guidelines.
Triclosan
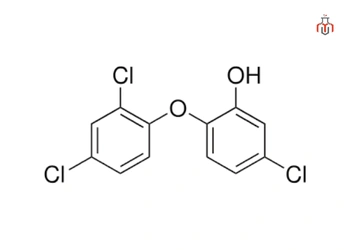
Triclosan is a synthetic, broad-spectrum compound added to soaps and toiletries for its antibacterial and antifungal properties, but in 2016, it was banned by the UDFDA for the sale of consumer antiseptic and wash products due to antimicrobial resistance and environmental impact.
Conclusion
Preservatives are essential ingredients added to cosmetics and personal care formulations to improve product safety, stability, and effectiveness throughout their shelf life. Cosmetic products are highly vulnerable to microbial contamination due to the presence of water, nutrient-rich ingredients, neutral pH, and repeated consumer use. Without preservatives, most cosmetic products get spoiled quickly, similar to perishable food. The controlled use of preservatives prevents spoilage, maintains product quality, and protects consumers from infections, irritation, and other adverse effects.
FAQs
Are preservatives safe for skin?
Preservatives added in cosmetics are generally safe as they are clinically checked by experts during formulation. However, patch tests must be performed as there are possible side effects in skin-sensitive individuals.
Are preservatives good or bad?
Preservatives are good as it helps to maintain the quality of the product and its shelf life. However, it can cause severe side effects on the skin and degrade the product quality upon high concentrations above the limit.
How much preservative to use in cosmetics?
The concentration of preservatives added to cosmetic formulations depends on the type of product, water content, and overall chemical composition of the formulation. In general, preservatives are used within the range of 0.3% to 1.0%, in accordance with applicable regulatory limits.
Why are preservatives added to cosmetics?
Preservatives are added to cosmetic formulations to prevent microbial growth, including bacteria, yeast, and mold, and to maintain the safety, effectiveness, and stability of products during storage and consumer use.
What are the three main types of preservatives?
Based on function, preservatives are categorised into three main types: antimicrobial, such as potassium sorbate and parabens, antioxidants, such as vitamin E (tocopherol), vitamin C (ascorbic acid) and anti-enzymatic preservatives such as EDTA and Sodium Metabisulfite.
Macschem is the leading supplier of Cosmetics Ingredients in the US.
Disclaimer:
The information provided is for general informational purposes only, based on publicly available sources, and does not constitute medical, regulatory, or professional advice. We disclaim any liability arising from its use without appropriate professional consultation.
Resources
Cosmetics Preservation: A Review on Present Strategies
Preservatives in Cosmetics: Regulatory Aspects and Analytical Methods


