
Niacinamide is a type of vitamin B3 that has a myriad of topical and dermatological uses. It is water-soluble, that is, the body does not store it and needs a regular supply via skincare or diet. Niacinamide is commonly found in foods like eggs, fish, and meat and is also used in cosmetic products such as lotions, creams and serums.
CAS No.: 98-92-0
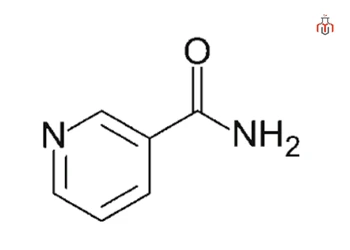
Synonyms: Nicotinamide, 3-Pyridinecarboxyamide, Pyridine-3-carboxyamide
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H6N2O |
| IUPAC name | 3-Pyridinecarboxyamide |
| Molecular weight | 122.12 g/mol |
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Bitter taste |
| Density | 1.400 g/cu cm at 25 °C |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | White powder |
| State | Dry powder |
| Boiling point | 334° C |
| Melting point | 128 – 131° C |
| LogP | -0.37 |
| pKa | 3.35 (at 20 °C) |
Strengthens skin barrier – Topical application of Niacinamide strengthens the protective layer of skin (Stratum corneum), which keeps the moisture in and irritants out, improves skin texture, regulates oil production and can reduce inflammation.
Reduces wrinkles and fine lines – Niacinamide boost collagen production, reducing fine lines and wrinkles.
Reduces inflammation – It is effective for the treatment of acne, sensitive skin and rosacea as it reduces redness and irritation.
Prevents Vitamin B3 deficiency – Vitamin B3 is essential to treat pellagra, a skin condition caused by niacin deficiency.
Topical Niacinamide
Oral supplement side effects
| Pictograms : |
|
| Hazard Statements : | H319: Causes serious eye irritation |
| Precautionary statements : | P264: Wash hands, eyes and face thoroughly after handling. |
Niacinamide is a type of vitamin B3 that has a myriad of topical and dermatological uses. It is water-soluble, that is, the body does not store it and needs a regular supply via skincare or diet. Niacinamide is commonly found in foods like eggs, fish, and meat and is also used in cosmetic products such as lotions, creams and serums.

CAS No.: 98-92-0
Synonyms: Nicotinamide, 3-Pyridinecarboxyamide, Pyridine-3-carboxyamide
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H6N2O |
| IUPAC name | 3-Pyridinecarboxyamide |
| Molecular weight | 122.12 g/mol |
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Bitter taste |
| Density | 1.400 g/cu cm at 25 °C |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | White powder |
| State | Dry powder |
| Boiling point | 334° C |
| Melting point | 128 – 131° C |
| LogP | -0.37 |
| pKa | 3.35 (at 20 °C) |
Strengthens skin barrier – Topical application of Niacinamide strengthens the protective layer of skin (Stratum corneum), which keeps the moisture in and irritants out, improves skin texture, regulates oil production and can reduce inflammation.
Reduces wrinkles and fine lines – Niacinamide boost collagen production, reducing fine lines and wrinkles.
Reduces inflammation – It is effective for the treatment of acne, sensitive skin and rosacea as it reduces redness and irritation.
Prevents Vitamin B3 deficiency – Vitamin B3 is essential to treat pellagra, a skin condition caused by niacin deficiency.
Topical Niacinamide
Oral supplement side effects
| Pictograms : |
|
| Hazard Statements : | H319: Causes serious eye irritation |
| Precautionary statements : | P264: Wash hands, eyes and face thoroughly after handling. |
Niacinamide is a multi-purpose skincare ingredient, improves hydration of the skin and can make it stronger by protecting the protective layer of the skin.
Niacinamide is good for acne; it helps regulate oil (sebum) production to prevent clogged pores, strengthens the skin barrier, reduces redness, minimizes pore appearance, and helps fade post-acne marks (hyperpigmentation). It also has strong anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce redness, swelling, and irritation in active acne.
Niacinamide can be used with vitamin C. Niacinamide helps regulate oil, strengthens the skin barrier, and reduces redness and inflammation, while vitamin C brightens the skin, boosts collagen, and provides antioxidant protection.