
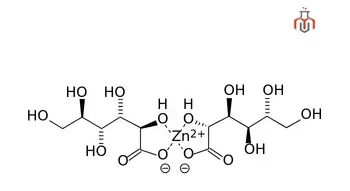
Zinc gluconate is the zinc salt of gluconic acid, composed of gluconic acid molecules and zinc ions. It plays a vital role in enzyme activity, immune function, protein and nucleic acid synthesis, and cellular proliferation.
It is widely used in multivitamin supplements, cosmetic formulations, and over-the-counter (OTC) medications, as a lozenge for the common cold. It is also used in fortified foods to promote healthy skin, hair, and nails, as well as to support protein synthesis (such as collagen in bone tissue), cell growth, and DNA formation.
CAS No: 4468-02-4
Synonyms: Zincum gluconicum, Zinkgluconaat, Rubozine, Zinc D-gluconate, Zeuterin
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C12H22O14Zn |
| IUPAC Name | zinc(2+) ion bis((2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate) |
| Molecular weight | 455.69 g/mol |
| State | Crystalline Solid to powder form |
| Boiling point point | 172-319°C |
| Melting point | 172-175°C |
| Density | 1.44 (at 20℃) |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | White |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol, and in methylene chloride |
| Odor | Odorless |
| pH | 6.5 |
| LogP | -7.41 at 20℃ |
| Flash point | >93.3 °C |
| Pictograms : |  |
| Hazard Statements : | H315 Causes skin irritation H319 Causes serious eye irritation H335 May cause respiratory irritation |
| Precautionary statements : | P273 Avoid release to the environment P391 Collect spillage P501 Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local/regional/national/international regulations |
Zinc gluconate is the zinc salt of gluconic acid, composed of gluconic acid molecules and zinc ions. It plays a vital role in enzyme activity, immune function, protein and nucleic acid synthesis, and cellular proliferation.
It is widely used in multivitamin supplements, cosmetic formulations, and over-the-counter (OTC) medications, as a lozenge for the common cold. It is also used in fortified foods to promote healthy skin, hair, and nails, as well as to support protein synthesis (such as collagen in bone tissue), cell growth, and DNA formation.

CAS No: 4468-02-4
Synonyms: Zincum gluconicum, Zinkgluconaat, Rubozine, Zinc D-gluconate, Zeuterin
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C12H22O14Zn |
| IUPAC Name | zinc(2+) ion bis((2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate) |
| Molecular weight | 455.69 g/mol |
| State | Crystalline Solid to powder form |
| Boiling point point | 172-319°C |
| Melting point | 172-175°C |
| Density | 1.44 (at 20℃) |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | White |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol, and in methylene chloride |
| Odor | Odorless |
| pH | 6.5 |
| LogP | -7.41 at 20℃ |
| Flash point | >93.3 °C |
| Pictograms : |  |
| Hazard Statements : | H315 Causes skin irritation H319 Causes serious eye irritation H335 May cause respiratory irritation |
| Precautionary statements : | P273 Avoid release to the environment P391 Collect spillage P501 Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local/regional/national/international regulations |
Zinc gluconate is easily absorbed by the body; however, its absorption can be reduced by phytates and the acidic environment of the stomach.
Zinc gluconate should not be mixed with the drugs that interact negatively with it, such as penicillamine, antibiotics like quinolones and tetracyclines, acid-reducing medication like omeprazole, and supplements containing iron (Fe), calcium (Ca), or magnesium (Mg). It is also advisable to avoid taking Zinc gluconate with foods high in phytates.
Zinc gluconate is freely water soluble. Its high water solubility makes it suitable for oral and intravenous formulations as well as liquid supplements.
Zinc is essential for testicular function and the synthesis of luteinizing hormone (LH), which stimulates testosterone production. However, Zinc gluconate is not intended to directly increase testosterone and should not be used as a substitute for treatment.
Taking too much zinc gluconate for a long time leads to adverse effects such as anemia and copper deficiency, and suppression of the immune response.
Zinc gluconate boosts immunity, protein, and DNA synthesis, wound healing, and helps reduce oxidative stress.