
Chlorhexidine is a broad-spectrum antiseptic and disinfectant belonging to the biguanide class of compounds. It is widely used in medical, dental, pharmaceutical, and personal care formulations due to its potent bactericidal and bacteriostatic properties. It is effective against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, some viruses, and fungi. Commonly available as chlorhexidine digluconate, chlorhexidine dihydrochloride, and chlorhexidine diacetate salts, it helps to reduce the swelling of gums, yeast infections of the mouth, oral rinses, and wound cleaning.
Chlorhexidine works by disrupting microbial cell membranes by binding with negatively charged phosphate groups on the cell wall. This action increases cell permeability, leading to the leakage of intracellular contents and ultimately, cell death. It has a high affinity for skin and mucous membranes, enabling sustained antimicrobial activity through prolonged residual binding.
Its mechanism makes it particularly valuable for reducing microbial load and preventing nosocomial infections in both clinical and personal care.
CAS No.: 55-56-1
Synonyms: Chlorhexidine Acetate, Tubulicid, Fimeil, Chlorhexidine Hydrochloride, Novalsan, Sebidin A
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C22H30Cl2N10 |
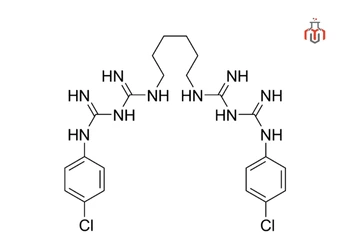
| IUPAC Name | 1,1′-Hexamethylenebis[5-(4-chlorophenyl)biguanide] |
| Molecular weight | 505.44 g/mol |
| Solubility | Soluble in organic solvents like DMSO, Ethanol Sparingly soluble in water |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.06 g/cm³ for digluconate solution |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | Colorless or Pale Yellow |
| State | Crystalline solids |
| Melting point | 134°C |
| pKa | 10.8 (at 25 °C) |
| LogP | 0.08 |
Used in surgical procedures to clean the skin, prepare catheter insertion sites, and rinse wounds to prevent infection.
In making veterinary products such as shampoos, wipes, and mousses to treat skin and paw infections in cats and dogs.
Included in anti-dandruff shampoos to help manage scalp dermatitis caused by Malassezia species.
Found in dental care products, including mouthwashes and gels, to control plaque and treat oral infections.
Applied in urinary catheter care to help reduce the risk of catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs).
| Pictograms : |
|
| Hazard Statements : | H318 Causes serious eye damage H410 Very toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effects |
| Precautionary statements : | P273 Avoid release to the environment P280 Wear eye protection/ face protection P305 + P351 + P338 IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes Remove contact lenses, if present, and easy to do. Continue rinsing. P391 Collect spillage P501 Dispose of contents/ container to an approved waste disposal plant |
Chlorhexidine is a broad-spectrum antiseptic and disinfectant belonging to the biguanide class of compounds. It is widely used in medical, dental, pharmaceutical, and personal care formulations due to its potent bactericidal and bacteriostatic properties. It is effective against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, some viruses, and fungi. Commonly available as chlorhexidine digluconate, chlorhexidine dihydrochloride, and chlorhexidine diacetate salts, it helps to reduce the swelling of gums, yeast infections of the mouth, oral rinses, and wound cleaning.

Chlorhexidine works by disrupting microbial cell membranes by binding with negatively charged phosphate groups on the cell wall. This action increases cell permeability, leading to the leakage of intracellular contents and ultimately, cell death. It has a high affinity for skin and mucous membranes, enabling sustained antimicrobial activity through prolonged residual binding.
Its mechanism makes it particularly valuable for reducing microbial load and preventing nosocomial infections in both clinical and personal care.
CAS No.: 55-56-1
Synonyms: Chlorhexidine Acetate, Tubulicid, Fimeil, Chlorhexidine Hydrochloride, Novalsan, Sebidin A
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C22H30Cl2N10 |
| IUPAC Name | 1,1′-Hexamethylenebis[5-(4-chlorophenyl)biguanide] |
| Molecular weight | 505.44 g/mol |
| Solubility | Soluble in organic solvents like DMSO, Ethanol Sparingly soluble in water |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.06 g/cm³ for digluconate solution |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | Colorless or Pale Yellow |
| State | Crystalline solids |
| Melting point | 134°C |
| pKa | 10.8 (at 25 °C) |
| LogP | 0.08 |
Used in surgical procedures to clean the skin, prepare catheter insertion sites, and rinse wounds to prevent infection.
In making veterinary products such as shampoos, wipes, and mousses to treat skin and paw infections in cats and dogs.
Included in anti-dandruff shampoos to help manage scalp dermatitis caused by Malassezia species.
Found in dental care products, including mouthwashes and gels, to control plaque and treat oral infections.
Applied in urinary catheter care to help reduce the risk of catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs).
| Pictograms : |
|
| Hazard Statements : | H318 Causes serious eye damage H410 Very toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effects |
| Precautionary statements : | P273 Avoid release to the environment P280 Wear eye protection/ face protection P305 + P351 + P338 IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes Remove contact lenses, if present, and easy to do. Continue rinsing. P391 Collect spillage P501 Dispose of contents/ container to an approved waste disposal plant |
Chlorhexidine is generally considered safe for human use at low concentrations in skin treatments, sprays, lozenges, and dental care treatments.
Chlorhexidine has antiseptic properties that eliminate bacteria and is commonly used to clean and disinfect open wounds, however, it should be applied only under medical supervision.
Chlorhexidine is mainly used in dental treatment for managing gingivitis, throat infections, and mouth ulcers. It is also used to cleanse the skin after an injury.
Chlorhexidine and hydrogen peroxide are chemically different compounds. Chlorhexidine is a broad-spectrum antiseptic used in mouthwashes to prevent plaque, while hydrogen peroxide is a strong oxidising agent, more common in minor cuts and general disinfection.
Chlorhexidine starts showing its effects immediately, within minutes, and it provides quick antimicrobial action and offers long-lasting protection for up to 6 hours. Due to its residual effect.
Long-term use of chlorhexidine may cause reversible staining of the teeth and tongue. It can also increase tartar buildup and temporarily alter taste. Regular dental cleaning can help prevent and lower these effects.