
Folic acid, also known as folate, is a type of B vitamin essential for human and animal health. The term “folate” is derived from folium, the Latin word for “leaf,” reflecting its abundance in leafy green vegetables. While folate occurs naturally in various foods, folic acid refers to the synthetic substitute widely used in dietary supplements, fortified food products, and nutraceuticals.
It is approved by the FDA for treating folic acid deficiency of megaloblastic and macrocytic anemias.
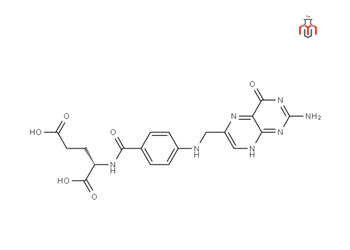
CAS No: 59-30-3
Synonyms: Vitamin B9, Folacin, Vitamin M, Pteroylmonoglutamic Acid, Pteroylglutamic Acid, Folate
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C19H19N7O6 |
| IUPAC Name | (2S)-2-[[4-[(2-amino-4-oxo-3H-pteridin-6-yl)methylamino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid |
| Molecular weight | 441.4 g/mol |
| State | Crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 250 °C |
| Storage | 2°C to 8°C |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | Yellowish orange |
| Solubility | Sparingly soluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol, insoluble in acetone, and in chloroform |
| Odor | Odorless |
| pH | 4-4.8 |
Folic acid, also known as folate, is a type of B vitamin essential for human and animal health. The term “folate” is derived from folium, the Latin word for “leaf,” reflecting its abundance in leafy green vegetables. While folate occurs naturally in various foods, folic acid refers to the synthetic substitute widely used in dietary supplements, fortified food products, and nutraceuticals.
It is approved by the FDA for treating folic acid deficiency of megaloblastic and macrocytic anemias.

CAS No: 59-30-3
Synonyms: Vitamin B9, Folacin, Vitamin M, Pteroylmonoglutamic Acid, Pteroylglutamic Acid, Folate
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C19H19N7O6 |
| IUPAC Name | (2S)-2-[[4-[(2-amino-4-oxo-3H-pteridin-6-yl)methylamino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid |
| Molecular weight | 441.4 g/mol |
| State | Crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 250 °C |
| Storage | 2°C to 8°C |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | Yellowish orange |
| Solubility | Sparingly soluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol, insoluble in acetone, and in chloroform |
| Odor | Odorless |
| pH | 4-4.8 |
Folic acid aids in the production of red blood cells and supports the proliferation of matrix keratinocytes in the hair bulb by facilitating DNA synthesis.
Folic acid and iron are not the same. Folic acid is a type of B-vitamin (vitamin B9) that helps with DNA synthesis and cell division, while iron is a mineral that supports the production of hemoglobin and helps carry oxygen in the blood.
Folate and folic acid are forms of vitamin B9, but folate is the naturally occurring form found in leafy vegetables, while folic acid is synthetic in origin and widely used in dietary supplements.
Folic acid is essential for cell division and DNA synthesis, red blood cell (RBC) formation, neural tube development, and the regulation of homocysteine levels.
A lack of folic acid in the body can lead to various health issues, like mouth sores, anemia, and neurological issues. In pregnant women, low folic acid increase the chances of neural tube defects in the baby.