
Cyanocobalamin is a synthesized form of vitamin B12 used to treat vitamin B12 deficiency. It promotes healthy brain and nerve function and is essential for the production of red blood cells (RBCs).
First synthesized in the 1940s, cyanocobalamin is now widely available as a generic drug and over-the-counter (OTC) supplement. It is one of the most commonly prescribed medications in the United States.
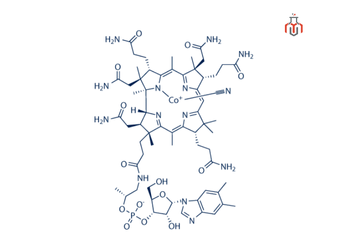
CAS No.:68-19-9
Synonyms: Vitamin B12, Cobalamin
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C63H88CoN14O14P |
| Molecular weight | 1355.4 g/mol |
| State | Crystalline or amorphous powder |
| Melting point | >300 °C |
| Storage | 2°C to 8°C |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | Dark red to reddish-purple |
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, insoluble in acetone, chloroform, and ether |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Tasteless |
| pH | 6 |
Cyanocobalamin is a synthesized form of vitamin B12 used to treat vitamin B12 deficiency. It promotes healthy brain and nerve function and is essential for the production of red blood cells (RBCs).
First synthesized in the 1940s, cyanocobalamin is now widely available as a generic drug and over-the-counter (OTC) supplement. It is one of the most commonly prescribed medications in the United States.

CAS No.:68-19-9
Synonyms: Vitamin B12, Cobalamin
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C63H88CoN14O14P |
| Molecular weight | 1355.4 g/mol |
| State | Crystalline or amorphous powder |
| Melting point | >300 °C |
| Storage | 2°C to 8°C |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | Dark red to reddish-purple |
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, insoluble in acetone, chloroform, and ether |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Tasteless |
| pH | 6 |
Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B12) supports healthy hair growth by promoting red blood cell formation, improving oxygen supply to hair follicles, and boosting scalp health.
Vitamin B12 and Cyanocobalamin both are used for common purposes, the only differences lie in their formation. Cyanocobalamine is a synthetic substitute of Vitamin B12, and methylcobalamin (Vitamin B12) is of natural origin.
A lack of cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B12) may cause megaloblastic anemia, fatigue, nerve damage, memory issues, and neurological disorders. Its long-term deficiency may lead to irreversible nerve damage if left untreated.
Cyanocobalamin is safe and well-tolerated. However, consult your healthcare provider before taking in use.