
Wright’s stain a unique dye employed for staining cells and tissues in laboratory settings. It is a mixture of eosin and methylene blue, which delivers a range of colors depending on the cellular components being stained. The stain produces a range of colors, from pink to purple, based on the pH and chemical composition of the cellular elements. Further, it is typically prepared as a solution and implemented on microscope slides to increase the visualization of cellular structures.
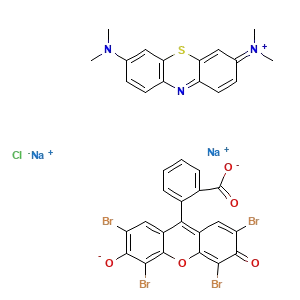
CAS No.: 68988-92-1
Synonyms: [7-(Dimethylamino)phenothiazin-3-ylidene] -dimethylazanium; 2-(2,4,5,7-tetrabromo-3,6-dihydroxyxanthen-10-ium-9-yl)benzoic acid; Tache de Wright; Mancha de Wright; Macchia di Wright; Tincion de Wright.
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C36H27Br4N3O5S |
| IUPAC Name | [7-(dimethylamino)phenothiazin-3-ylidene]-dimethylazanium;2-(2,4,5,7-tetrabromo-3,6-dihydroxyxanthen-10-ium-9-yl)benzoic acid |
| Molecular weight | 933.3 g/mol |
| Solubility | Water and Alcohol |
| Flash point | 11°C |
| Density | 0.8 |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Colour | Dark Green |
| State | Powder |
| Melting point | 19.85°C |
| λmax | 500-520 nm |
| Vapor pressure | 97.68 mmHg at 20°C |
| Vapor density | 3.17 |
| Explosion Limit lower | 6% |
| Explosion Limit upper | 36.50% |
| Pictograms : |  |
| Hazard Statements : | H302: Harmful if swallowed |
| Precautionary statements : | P280: Wear protective gloves/eye protection |
Wright’s stain a unique dye employed for staining cells and tissues in laboratory settings. It is a mixture of eosin and methylene blue, which delivers a range of colors depending on the cellular components being stained. The stain produces a range of colors, from pink to purple, based on the pH and chemical composition of the cellular elements. Further, it is typically prepared as a solution and implemented on microscope slides to increase the visualization of cellular structures.

CAS No.: 68988-92-1
Synonyms: [7-(Dimethylamino)phenothiazin-3-ylidene] -dimethylazanium; 2-(2,4,5,7-tetrabromo-3,6-dihydroxyxanthen-10-ium-9-yl)benzoic acid; Tache de Wright; Mancha de Wright; Macchia di Wright; Tincion de Wright.
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C36H27Br4N3O5S |
| IUPAC Name | [7-(dimethylamino)phenothiazin-3-ylidene]-dimethylazanium;2-(2,4,5,7-tetrabromo-3,6-dihydroxyxanthen-10-ium-9-yl)benzoic acid |
| Molecular weight | 933.3 g/mol |
| Solubility | Water and Alcohol |
| Flash point | 11°C |
| Density | 0.8 |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Colour | Dark Green |
| State | Powder |
| Melting point | 19.85°C |
| λmax | 500-520 nm |
| Vapor pressure | 97.68 mmHg at 20°C |
| Vapor density | 3.17 |
| Explosion Limit lower | 6% |
| Explosion Limit upper | 36.50% |
| Pictograms : |  |
| Hazard Statements : | H302: Harmful if swallowed |
| Precautionary statements : | P280: Wear protective gloves/eye protection |
Wright’s stain differentiates cell components by using eosin to stain acidic parts red and methylene blue to stain basic parts blue, aiding in the identification of blood cell types under a microscope.
Wright’s stain may not effectively visualize certain intracellular structures, such as small organelles, definite bacteria, or fungi.
The buffer in Wright’s stain helps maintain a stable pH during the staining process, ensuring proper differentiation of blood cell components and accurate coloration.
In parasitology, Wright’s stain is used for identification & differentiating parasites, particularly blood-borne parasites like Plasmodium (malaria) and Trypanosoma species, by staining their cellular structures in blood smears.