
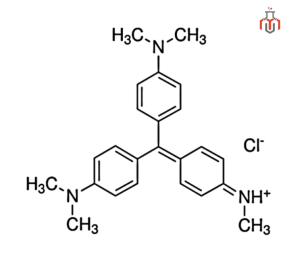
Methyl Violet 2B is a synthetic triphenylmethane dye known for its intense violet color and broad applications in microbiology, textiles, industry, and chemical research. It is widely used as a biological stain, pH indicator, and dye for fabrics, inks, and coatings. It is a greenish powder that is soluble in water and ethanol, and its color changes depending on the pH of the solution.
CAS No.: 8004-87-3
Synonyms: Basic Violet 1, C.I 42535, Tetraamethylparosanilinium chloride
Resources: Biological Stains | Classification, Examples & Uses
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C23H26N3Cl |
| IUPAC Name | 4,4′-[(4-Imino-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-yliden)methylen]bis(N,N-dimethylaniline)hydrochloride |
| Molecular weight | 344.5 g/mol |
| Solubility | Soluble in Water & Ethanol Insoluble in Xylene |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Colour | Green to Dark Green |
| State | Crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 137 °C |
| λmax | 580 nm+/-20 nm |
| pka | 0.8 |
Acute Toxicity: It can cause skin irritation, eye damage, and respiratory issues if inhaled or ingested. Prolonged exposure may lead to nausea, dizziness, or allergic reactions.
Aquatic Toxicity: It is highly toxic to aquatic organisms, causing environmental hazards if released into water systems. It can disrupt marine ecosystems and bioaccumulate in aquatic life.
Mutagenicity: It may cause genetic mutations in cells, posing risks for DNA alterations and long-term health effects.
| Pictograms : |
|
| Hazard Statements : | H302: Harmful if swallowed. |
| Precautionary statements : | P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. |
Methyl Violet 2B is a synthetic triphenylmethane dye known for its intense violet color and broad applications in microbiology, textiles, industry, and chemical research. It is widely used as a biological stain, pH indicator, and dye for fabrics, inks, and coatings. It is a greenish powder that is soluble in water and ethanol, and its color changes depending on the pH of the solution.

CAS No.: 8004-87-3
Synonyms: Basic Violet 1, C.I 42535, Tetraamethylparosanilinium chloride
Resources: Biological Stains | Classification, Examples & Uses
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C23H26N3Cl |
| IUPAC Name | 4,4′-[(4-Imino-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-yliden)methylen]bis(N,N-dimethylaniline)hydrochloride |
| Molecular weight | 344.5 g/mol |
| Solubility | Soluble in Water & Ethanol Insoluble in Xylene |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Colour | Green to Dark Green |
| State | Crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 137 °C |
| λmax | 580 nm+/-20 nm |
| pka | 0.8 |
Acute Toxicity: It can cause skin irritation, eye damage, and respiratory issues if inhaled or ingested. Prolonged exposure may lead to nausea, dizziness, or allergic reactions.
Aquatic Toxicity: It is highly toxic to aquatic organisms, causing environmental hazards if released into water systems. It can disrupt marine ecosystems and bioaccumulate in aquatic life.
Mutagenicity: It may cause genetic mutations in cells, posing risks for DNA alterations and long-term health effects.
| Pictograms : |
|
| Hazard Statements : | H302: Harmful if swallowed. |
| Precautionary statements : | P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. |
It is commonly used to dye textiles such as cotton, silk, and leather, providing purple and deep violet colors.
Methyl Violet 2B is used for dyeing textiles and paper, biological staining for bacterial classification, and as a pH indicator. It also stains human lung fibroblast cells in antiviral assays.
If swallowed, methyl violet 2B can be harmful and irritate the eyes, skin, and respiratory system. It is also toxic to aquatic life if used in the long term.
If inhaled, it can harm the skin and eyes and cause respiratory issues. Prolonged exposure can also make it potentially carcinogenic.
Due to its harmful properties, it should be handled with care and used according to safety guidelines to avoid health risks.
It is primarily used as a biological stain in microscopy, a pH indicator, and an antimicrobial agent. It is also used in textile dyeing, ink manufacturing, and forensic analysis to detect specific substances.
Crystal violet is the fully methylated form of methyl violet. It has more methyl groups attached to its molecules than methyl violet. Also, Methyl Violet is bluish-purple, while crystal violet is dark violet.
Methyl Violet 2B dissolves easily in water, producing a violet-colored solution, and is also soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and methanol.